It is amazing that some people would get confused about the second largest continent in the World and would ask “is Africa a country or a continent?” Africa is not a country but a continent and one of the major ones in that regard. It is not like Australia that is a country as well as a continent.
The misconception in thinking that Africa is a country rather than a continent is fueled by the media and those who more often than not project Africa as a country damaged by war, famine and corruption. Africa is a continent with 54 different countries that it supports. The largest black continent in the world and home to more than 1 billion people in the world hence 1 in 7 of any human on earth is an African.
Is Africa a Country? Why Africa is not A Country
Africa is a disintegrated and segmented group of people that has been, even before the name Africa evolved. They appear as species of their own kind following different fathers & origins and in connection with their black Races… In answering the question “is Africa a country?” It is noteworthy that the origin of Africa cannot be traced to a singular entity. The appearance & race of Africans are meant to keep the populace recognized as a country, but the various tongues & origin has made them of different groups, and with this, they are not fit to be called a country. Taking the variations in language for instance, England could be looked at as one of the countries which appeared as a true unified country when language and origin is carefully considered and when the same factors are used in the case of Nigeria, it would mean that Nigeria would rather be recognized as a continent because of the various origins and differences in the language of its citizens. Generally speaking, a continent is, therefore, a body of land that is home to many different countries with its boundaries being divided based on geography. This, of course, excludes Australia and Antarctica, which stand on their own. A country, on the other hand, is actually part of a continent that has its boundaries being determined by people, although sometimes these boundaries are disputed.
In essence, Africa is not a country but a continent with over 50 independent countries that are internationally recognized. Below is a list of countries in Africa.
List of African Countries
- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Congo
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Cote d’Ivoire
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- Sao Tome and Principe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- Sudan (North)
- South Sudan (Rep.)
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
See Also: Get To Know The Political Term Limits In Various African Countries
Regions in Africa
Added to the division of the continent into different independent countries, it is also important to note that Africa, like in Asia, is divided into regions. Many public figures and journalists have also confused a region in Africa with the countries in that region. For instance, when referring to a crisis in a region in Africa and how it affects the nearby countries instead of its equivalent region. A region, geographically speaking, is a subset of a continent made up of a group of countries.
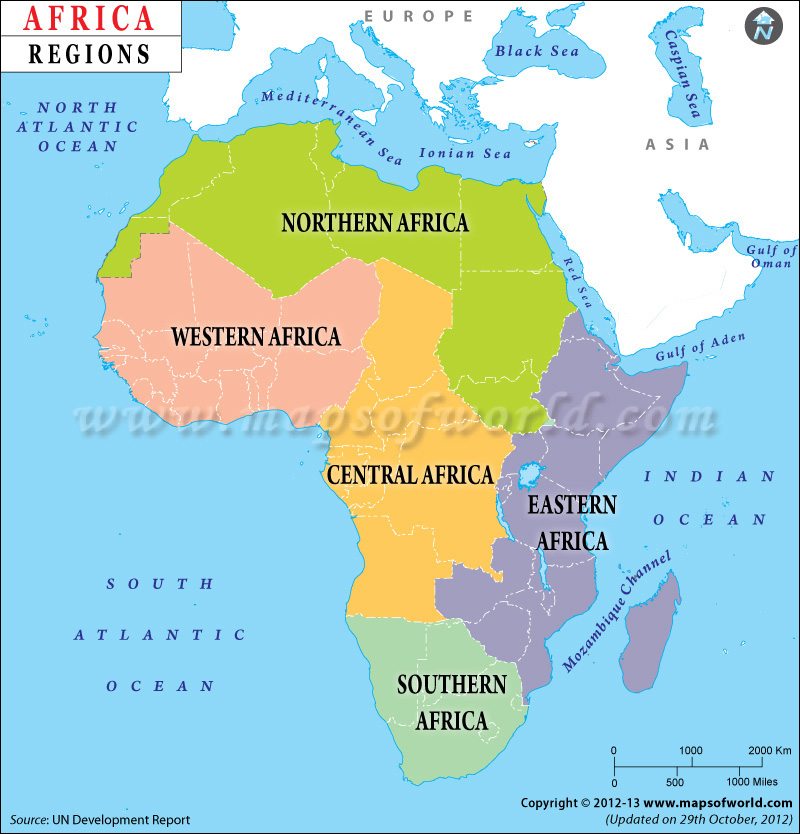
Africa as a continent is commonly divided into five geographically recognised regions which include Northern Africa, Western Africa, Central Africa, Eastern Africa and Southern Africa. Below is a list of countries that fall under each region.
Northern Africa
This is the northmost region of Africa. Three predominant factors in this region are religion and environment. The region is surrounded by deserts and Islam is its predominant religion. In terms of the season, North Africa experience their spring in the months of March, April, May; Summer in June, July, August; Autumn in September, October, November; and Winter in December, January, February. The 7 countries in North Africa include:
- Algeria
- Egypt
- Libya
- Morocco
- Sudan
- Tunisia
- Western Sahara
Southern Africa
A lot of people think the Southern African region is another name for South Africa. This is not true, Southern Africa is the region of the African continent south of the Congo and Tanzania, while South Africa is just a country in the region. Among other factors that determine the mapping of this region, Southern Africa has its spring in August, September, October; Summer in November, December, January; Autumn in February, March, April; and Winter in May, June, July. There are 10 countries in this part of the continent:
- Angola
- Botswana
- Lesotho
- Malawi,
- Mozambique,
- Namibia,
- South Africa,
- Swaziland,
- Zambia,
- Zimbabwe.
Eastern Africa
The history of the region called East Africa goes way beyond stories about the animals, land rovers, beaches, luxury safari tents and the 5 pm sundowners. No doubt, East Africa is a region with as diverse and as abundant terrestrial mammals, hence it is also called the Great Lakes Region. However, there are more to it. , East Africa is a region located in the Eastern part of the African continent with parts of it extending to cover a prominence on the African map called the horn of Africa. Although Egypt is technically on the eastern side of Africa, it is usually considered part of North Africa rather than East Africa. Below are the countries in East Africa:
- Burundi
- Comoros,
- Djibouti,
- Ethiopia,
- Eritrea
- Kenya
- Madagascar
- Mauritius
- Malawi
- Mayotte
- Mozambique
- Rwanda
- Reunion
- Seychelles
- South Sudan
- Somalia,
- Uganda
- Tanzania
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
Western Africa
This region is described as one of the world’s most diverse and fascinating regions. It is a part of the African continent that is predominantly dominated by black people. Aside from its cultural diversities, the West Africa or Western African region is rich in natural resources and is made up of the Sahel region (semi-arid savannas) and tropical forests and grasslands.
The region comprises of eighteen countries including the Island of Saint of Helena which is recognized as a British overseas territory and the Portuguese-colonized Democratic Republic of Sao Tome and Principe. The countries in West Africa therefore include:
- Benin
2. Mali
3. Burkina Faso
4. Mauritania
5. Ivory Coast
6. Niger
7. Cape Verde
8. Nigeria
9. Gambia
10. Senegal
11. Ghana
12. Sierra Leone
13. Guinea
14. Saint Helena
15. Guinea Bissau
16. Sou Tome &Principe
17. Liberia
18. Togo
Central Africa
Central Africa is the core or central region of the African continent. It should not be confused with the Central African Republic (CAR) which is a landlocked country in central Africa. In comparison, the area occupied by the Central African Republic is slightly smaller than the state of Texas. The countries in this region include:
- Gabon,
- Cameroon
- Chad
- The Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- Equitorial Gunea
- Rwanda,
- Burundi,
- São Tomé and Príncipe,
- The central African Republic
See Also: List Of African Currencies You Really Should Know
Languages in Africa
In addition to the division of the landmass into different regions and countries, the African continent is also a home to the highest linguistic diversity in the world, with over 1500 different languages. In other words, not only is Africa the second most populous continent in the world with over one billion people, it is the most linguistically diverse continents in the world. These languages form part of the four major language groups, namely Afro-Asiatic covering Northern Africa, Central Sahara and the Horn of Africa, Nilo-Saharian covering Central and Eastern Africa, Niger-Congo covering Central, Southern and Eastern Africa and Khoisan, covering the Western part of Southern Africa.
However, the principal languages on the continent include Arabic, French and English with French being the most widely spoken language in Africa. In Sum, here are the eleven most spoken languages in Africa
- Arabic – A Central Semitic language that first emerged in Iron Age northwestern Arabia and is now the official language of the Arab world. The language is widely spoken by over 280 million people worldwide with African countries such as Egypt, Algeria, Morocco, Mauritania, Libya, Eritrea and more using it as their official language.
- Swahili – A Bantu language believed to have originated from other languages, mainly Arabic, due to historical interactions between Arabs from the Middle East and East Africans. The language is spoken by over 100 million people in the continent.
- Amharic – The official language of Ethiopia and the second most spoken language in the world. The language is spoken by over 21 million people.
- Yoruba – The third most widely spoken language in the African continent, accounting for over 30 million speakers in Nigeria, Benin and Togo. The language with over fifteen dialects including Awori, Ijesha, Ilaje and Ila, is also widely spoken in part of western countries like the US and UK.
- Oromo – A language spoken by over 30 million people, particularly those Horn of Africa and parts of East Africa like Ethiopia, Kenya and Somalia.
- Hausa – One of the most spoken Chadic languages with over 40 million native and second language speakers. It is one of Nigeria’s three official languages. Countries that speak this language include Nigeria, Niger, Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, CAR, Chad, Congo, Eritrea, Germany, Ghana, Sudan, Togo and much of North Africa.
- Igbo – The third official language in Nigeria. It is also spoken by over 20 million people, with a significant amount of speakers in Cameroon and Equatorial Guinea.
- IsiZulu, or Zulu – One of the official languages in South Africa. The language is also part of the Nguni subgroup of the Bantu language and is widely spoken by over 10 million people, particularly in Eastern South Africa.
- Shona – The most widely spoken Bantu language as a first language and is native to the Shona people of Zimbabwe. The language is also spoken in Botswana and Mozambique.
- Portuguese – The official language of six African states, including Angola, Mozambique, Guinea-Bissau, Cape Verde, Sao Tome and Principe and Equatorial Guinea.
- French – The official language of about 26 African countries and spoken by over 120 million people. Countries like Gabon, Mauritius, Cote d’Ivoire, Senegal, Sao Tome e Principe, Tunisia, Guinea, Seychelles, Democratic Republic of Congo and Equatorial Guinea either use the language as their mother tongue or secondary language. However, Algeria remains the second largest French-speaking country with over 50 percent of the population being French speakers.
- English – Spoken by over a dozen African countries which include Uganda, Nigeria, Zambia, Botswana. Namibia, Kenya, Sierra Leone, Liberia, South Africa, and Zimbabwe. A large number of countries where English is the official language are the British Empire former territories but a country like Rwanda which was an Italian colony uses English and Kinyarwanda as its official languages.
