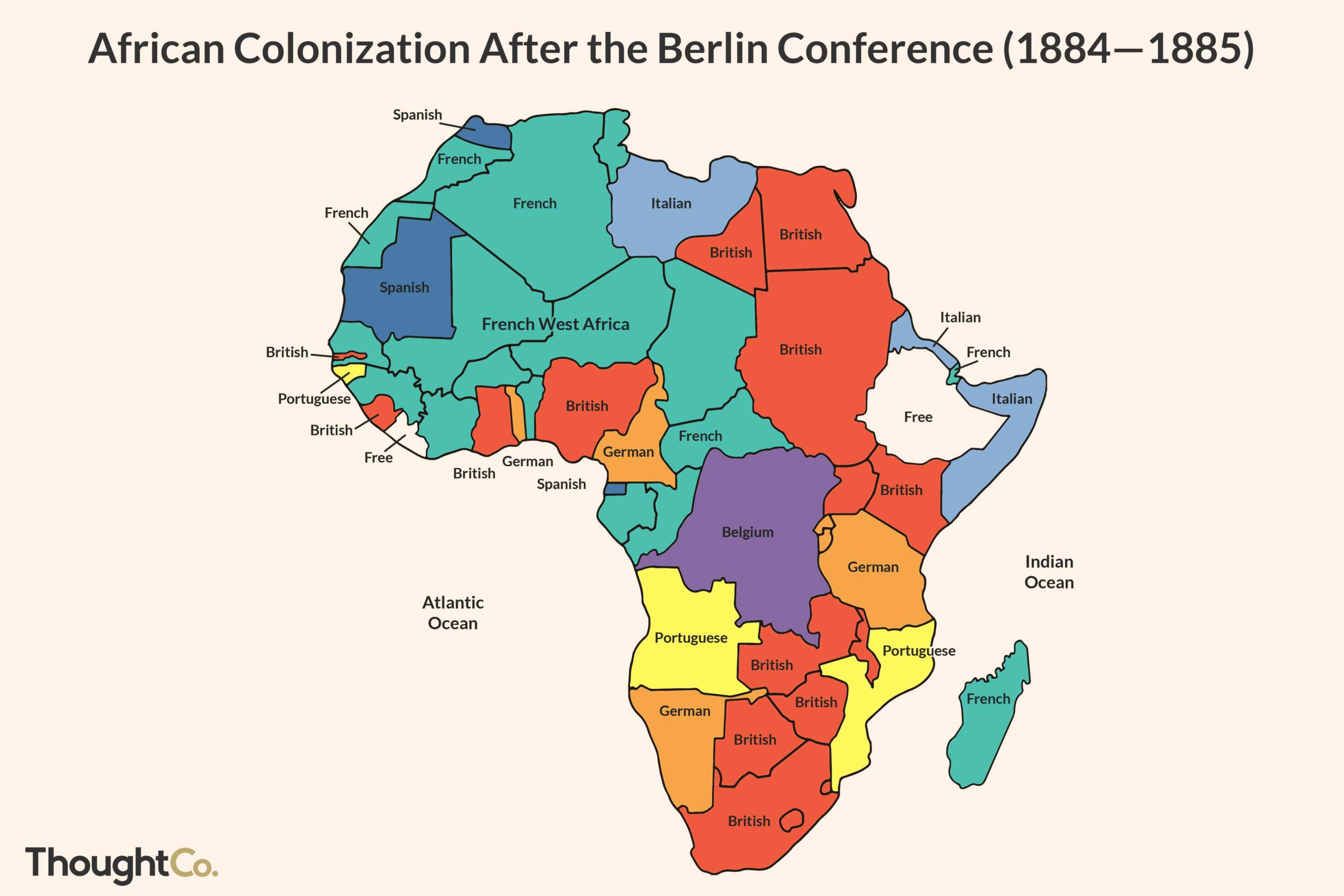
Thirteen European countries came together in the year 1884 to decide how Africa would be colonized. This meeting, now known as the Berlin Conference, was held in the city of Berlin and as a result of it, there are several European languages spoken in Africa as official languages because the colonized country usually takes on the language of the “colonizer”. France and Great Britain appear to have gotten a lion’s share as there are more French and English-speaking countries on the continent than any other language.
How Many English-Speaking Countries Are In Africa?
There are currently 25 English-speaking countries in Africa. The majority of the countries that speak English on the continent were former British colonies, while others adopted the language despite not being colonized by Britain, or colonized at all, like Ethiopia.
Ethiopia is English-speaking but was never colonized. Additionally, Eritrea, Burundi, and Rwanda are English-speaking countries despite being colonized by Italy and Belgium. Furthermore, Sierra Leone and Liberia speak English as a primary dialect because they are countries that were established by freed slaves. Cameroon is both English-speaking and French-speaking due to the fact both France and Britain colonized the country simultaneously. Egypt is a particularly exceptional case. English is neither an official language nor a part of the official languages. Arabic and Egyptian Arabic are the official and recognized languages in Egypt yet quite a sizeable number of the Egyptian population speak English.
With a total of 52 countries on the African continent, and 25 of them being English-speaking, (English is an official or one of the official languages in about 25 African countries) putting into consideration the population of each country by its English speakers (six of the ten most populous countries in Africa, have English as their official language) English is the second most widely spoken foreign language in the African continent. It is closely followed by French. Arabic is the most widely spoken language in Africa.
List of English-Speaking Countries in Africa
1. Ghana
- Colonized By: Britain
- Population: 31 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers: 66 percent
- Other Languages Spoken: Akan/Twi, Ewe, Frafra, Nzema, Dagaare, Dagbani, Ga, Hausa, Dangme, Asante

With over 60% of Ghana’s population being English speakers, English is very much widely spoken in Ghana. However, the most widely spoken language in Ghana is the Akan/Twi language. Over 80% of Ghana’s population speak Akan. English language is associated with literacy levels, as Ghana’s educational system and curriculum at all levels of Education are instructed in the English language. English became an official language in Ghana, as an inheritance of colonialism.
2. The Gambia
- Colonized By: Britain
- Population: 2.1 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers: 2.34 percent
- Other Languages Spoken: Wolof, Mandinka, Fula, Jola, Portuguese creole

However, the most widely spoken language is Mandinka. 38% of a larger part of The Gambia’s population communicate in Mandinka, followed by Fula 24% and Wolof 18%. English boasts of slightly over 2% and it is associated with literacy levels as it is the official language for instruction in Gambian Schools.
English is mostly only widely spoken in major cities like the Capital Banjul, and popular tourists towns like Bijilo, Bakau, and Jufereh. Yahya Jammeh, the former Gambian President once planned to drop English as the official language.
3. Liberia
- Colonized By: NIL
- Population: 4.9 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers: 82.67 percent
- Other Languages Spoken: Liberian English

Almost everyone in Liberia speaks English, over 80% of the entire Liberian population. This is due to Liberia’s history as a land founded by former slaves. Schools and education systems, at all levels, are instructed in English. However, the Kru, Kpelle, Mandingo, and Grebo ethnic languages are also spoken, with Kpelle being the most widely spoken amongst the native languages. But none of the languages form a distinct majority because since Liberia became an official country in 1824, English has been its official language.
4. South Africa
- Colonized By: Britain
- Population: 59 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers: 34 percent
- Other Languages Spoken: Afrikaans, Zulu, Xhosa, Ndebele, Venda, Tswana, Southern Sotho, Northern Sotho, Tsonga, Swati, Khoe, Nama, Khoisan

South Africa has 11 official languages, including English. The country also has three different cities as capitals. Of all the 11 official languages, English is the fourth most common language with 9% of South Africans speaking English as their first language. The most common language in South Africa and most widely spoken as the first language is Zulu, taking 24.7% of the population. Xhosa has 15% while Afrikaans has 12%. But English has been South Africa’s official language since it became a British colony. The country’s educational system is instructed in English and as such English language is associated with education and literacy.
5. Sierra Leone
- Colonized By: Britain
- Population: 7.9 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers: 83.53 percent
- Other Languages Spoken: Krio/Creole

Sierra Leone has had English as its De Facto official language since British occupation and colonization of the country. With over 80% of the population speaking English, Krio/Creole is the most widely spoken language in Sierra Leone. 97% of the country speak Krio, a variation of English that is mixed with nearby African languages. Other local languages spoken are Mende with 31% and Temme with 37%. English is also the language of the educational system and as such associated with literacy.
6. Uganda
- Colonized By: Britain
- Population: 45.7 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers: 21%
- Other Languages Spoken: Swahili, Luganda

Named in 2017 as the Best English-speaking African Country by the World Linguistic Society, Uganda uses English as its language of educational instruction across all levels of education. English is also associated with high social status and class in Uganda, and as such, English Language is associated with literacy.
7. Kenya
- Colonized By: Britain
- Population: 54.7 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers: 18.83 percent
- Other Languages Spoken: Swahili, Gikuyu, Oluluyia, Arabic

Both Swahili and English are languages for educational instruction and so both languages are associated with literacy. Swahili is mostly used in lower school classes for instructions whilst English language is taught as a subject, to prepare pupils for the introduction of English as a language of instruction in higher classes.
8. Nigeria
- Colonized By: Britain
- Population: 206 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers: 53.34 percent
- Other Languages Spoken: Igbo, Hausa, Yoruba

The most widely spoken native language in Nigeria is Hausa, as close to 30 million people speak Hausa while about 24 million speak Igbo and 19 million speak Yoruba. However, over 190 million people speak English in Nigeria as a second language. The highest number of English speakers can be found in the Southern Part of Nigeria, due to their first contact with the British. Although English is also spoken in Northern Nigeria, Arabic is taught in some schools in the North as an elective as it is associated with the Islamic Religion which is dominant in the North. French is also a subject taught in most schools in Nigeria.
9. Zimbabwe
- Colonized By: Britain
- Population: 14.8 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers: 89 percent
- Other Languages Spoken: Shona, Ndebele, Xhosa, Tswana, Venda, Chewa, Tsonga, Tonga, Kalanga, Sotho, Ndau, Khoisan, Shangani, Chibarwe

Less than 5% of Zimbabweans speak English as a first language, however, 89 percent of Zimbabweans speak English as their second language. Shona is spoken by almost 11 million Zimbabweans, followed by the Ndebele language which is spoken by over 20% of Zimbabweans. However, English is the language for both the government and the educational system, as such English is associated with literacy levels.
10. Rwanda
- Colonized By: Belgium
- Population: 12.9 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers: 15 percent
- Other Languages Spoken: French, Swahili, Kinyarwanda

By 2008, the government changed the medium of education from French to English and as such, English and French are both currently associated with literacy and education. Swahili is widely taught in schools, whilst Kinyarwanda is the most widely spoken language, with about 98% of the population using the language. 15% of the population speak English as a second language, with 0.2% as their first language. French is being spoken by a very minute population mostly amongst the educated.
11. Cameroon
- Colonized By: France
- Population: 26.5 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers: 17 percent
- Other Languages Spoken: French, Fula, Ewondo, Cameroon Pidgin English

The Anglophone population of Cameroon is in regression, according to a 2015 survey. The English speaking population regressed from 21% in the 1970s to 17% in 2015. However, currently, 80% of Cameroon speak French while the rest are English speakers. About 50% of Cameroon’s population speak Cameroonian pidgin English. Both English and French are the languages associated with literacy and education based on the particular former colony region.
12. Zambia
- Colonized By: Britain
- Population: 18.3 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers: 16.02 percent
- Other Languages Spoken: Bemba, Nyanja, Tonga, Lozi, Chewa

On the native languages, according to a 2000 census, Nyanja is the most widely spoken language with about 37% of Zambians speaking the language both as a first and second language. Bemba also has 35% of the population speaking it as a first and second language.
13. Eswatini (Swaziland)
- Colonized By: Britain
- Population: 1.1 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers: 4.83 percent
- Other Languages Spoken: Swati, Zulu

14. Tanzania
- Colonized By: Britain
- Population: 59.7 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers: 9.98 percent
- Other Languages Spoken: Swahili, Arabic, Maasai

15. Namibia
- Colonized By: South Africa
- Population: 2.55 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers: 17.24 percent
- Other Languages Spoken: Afrikaans, Otjiherero, Khoekhoe, German, Oshiwambo

At the dawn of Namibia’s independence in 1990, the founding fathers chose English as an official language to serve as a unifying factor. The school and educational system is also instructed in English, thereby associating English with literacy. However, for any visitor to Namibia, an added knowledge of the German language and Afrikaans would prove useful; because despite English being an official language, German and Afrikaans are still very much widely spoken. For the native language, close to 50% of Namibians speak Oshiwambo as a home language.
16. Sudan
- Colonized By: Britain
- Population: 43.8 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers: Undocumented
- Other Languages Spoken: Arabic, Hausa

There are lots of indigenous languages spoken in Sudan, but over half of the country’s population speak Arabic. Despite inheriting English as a colonial language, Arabic was the official language for educational instructions at all levels until 2005 when English and Arabic became the official working languages in Sudan and currently, both languages are used in Sudan’s educational system. As a result, English and Arabic are both associated with literacy levels.
17. South Sudan
- Colonized By: Britain
- Population: 12 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers: undocumented
- Other Languages Spoken: Luo, Dinka, Juba Arabic, Acholi, Zande, Bari

18. Seychelles
- Colonized By: Britain
- Population: 99 Thousand
- Percentage of English Speakers: 37.93 percent
- Other Languages Spoken: French, Seychellois Creole

For over a century since it was colonized, English was the only official language until the introduction of Creole in 1976, after Seychelles gained independence. 90% of the Seychelles population speak Seychellois Creole. The three official languages have snce become English, French, and Creole which are adapted into the educational system. Creole is used as a mode of instruction in the early years while English is introduced at the primary level. French comes in later on.
19. Lesotho
- Colonized By: Britain
- Population: 2.1 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers: 27.86
- Other Languages Spoken: Sesotho

Despite inheriting English as a former British colony, Sesotho is still the primary first language of over 90% of Lesotho’s population. English is mostly reserved for official interactions, and also in the governmental administration. English is associated with higher education in Lesotho because the first four years of primary education are instructed in Sesotho, with English introduced in the fifth year and later on. Competency in English is a prerequisite for political, educational, and economic transactions.
20. Mauritius
- Colonized By: Britain
- Population: 1.2 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers: 15.97 percent
- Other Languages Spoken: French, Mauritian Creole, Bhojpuri

Mauritius is both English and French-speaking, but the only “official” language is English. The majority of the Mauritian population speak French-based Mauritian creole; which is spoken by close to 90% of the population. English is spoken in the parliament as an official language and also as a medium of instruction in public schools since 1944. However, French is a dominant language of the media and also a common language in education. A 2005 study estimated French speakers at over 70%.
English and French are both recognized languages in Mauritius, but the English language has an upper hand as important texts and documentations, especially in the government and parliament and even education, are written in English.
21. Malawi
- Colonized By: Britain
- Population: 19.5 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers: 4.9 percent
- Other Languages Spoken: Chichewa, Yao, Tumbuka, Tonga, Sena, Lomwe

In 2014, English language was announced as the main language of instruction from primary school whilst still being taught as a core subject.
22. Burundi
- Colonized By: Belgium
- Population: 11.8 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers: 1 percent
- Other Languages Spoken: Swahili, French, Kirundi

About 98% of Burundians speak Kirundi. French is the language of educational instruction in Burundi, with English being taught as a core subject.
23. Eritrea
- Colonized By: Italy, Britain, Ethiopia
- Population: 3.5 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers:
- Other Languages Spoken: Tigrinya, Arabic, Afar, Tigre, Beja

Tigrinya is the most widely spoken language in Eritrea. Over 70% of Eritreans speak Tigrinya. English language is the medium of instruction from middle school in Eritrea. It was made the official language of instruction in Eritrean institutions of education in 1991, after its independence, however, the language was introduced by the British military rule in the Mid 1900s.
Arabic is also one of the main working languages in Eritrea. In fact, Tigrinya, Arabic and English are sited as the official languages of Eritrea according to the CIA Factbook. For literacy, English is not the very first call as Eritrea’s main orthography is the Ge’ez script, Latin and Arabic Script. Furthermore, names, instructions, traffic signs, and basic notices in Eritrea are all written or announced in Tigrinya, Arabic, and English.
24. Ethiopia
- Colonized By: NIL
- Population: 117.2 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers: 0.22 percent
- Other Languages Spoken: Amharic, Afar, Oromo, Tigrinya, Somali, Harari, Sidama

The use of English in Ethiopia is still a curious case, as it is not associated with colonialism, yet the number of English speakers is constantly on the increase. English was adopted as a medium of Western educational instruction after Haile Selassie in the early 1900s went to Britain on exile, and sought support from British against the Italian occupation of Ethiopia. This strengthened the British influence and by the 1950s, the British influenced the Ethiopian Western Educational system, and by large English language was established.
25. Botswana
- Colonized By: Britain
- Population: 2.3 Million
- Percentage of English Speakers: 38.42 percent
- Other Languages Spoken: Setswana

English is also associated with literacy and education as the country’s educational system is instructed in English. Only about 2% of the Botswana population speak English as a first language, however, a sizeable number of the population speak English as a second language.
Which Country Has The Most English Speakers In Africa?
Calculating the number of people who can speak English based on the number of the overall population in the country; the country with the most English speakers in Africa is Nigeria. Nigeria is the most populous country in Africa with over 206 million people.
According to WorldAtlas, 198 million people in Nigeria speak English, making it the country with the most English speakers in Africa. Nigeria is closely followed by Ethiopia with 108 million English Speakers, Tanzania with 60 Million, South Africa with 58 Million, and Kenya with 50 million.